We all know JWTs are vulnerable to attacks, there are many alternatives to it. But, we can improve our security mechanism by NOT storing the tokens in the browser.
Technique
We can use a counter which is mapped to a specific token. When creating a cookie, the value of this counter is given instead of the token itself. This way, the token stays on the server.
As we can see this is kind of a key-value relationship, for this Redis is quite a good choice. Also, it is scalable.
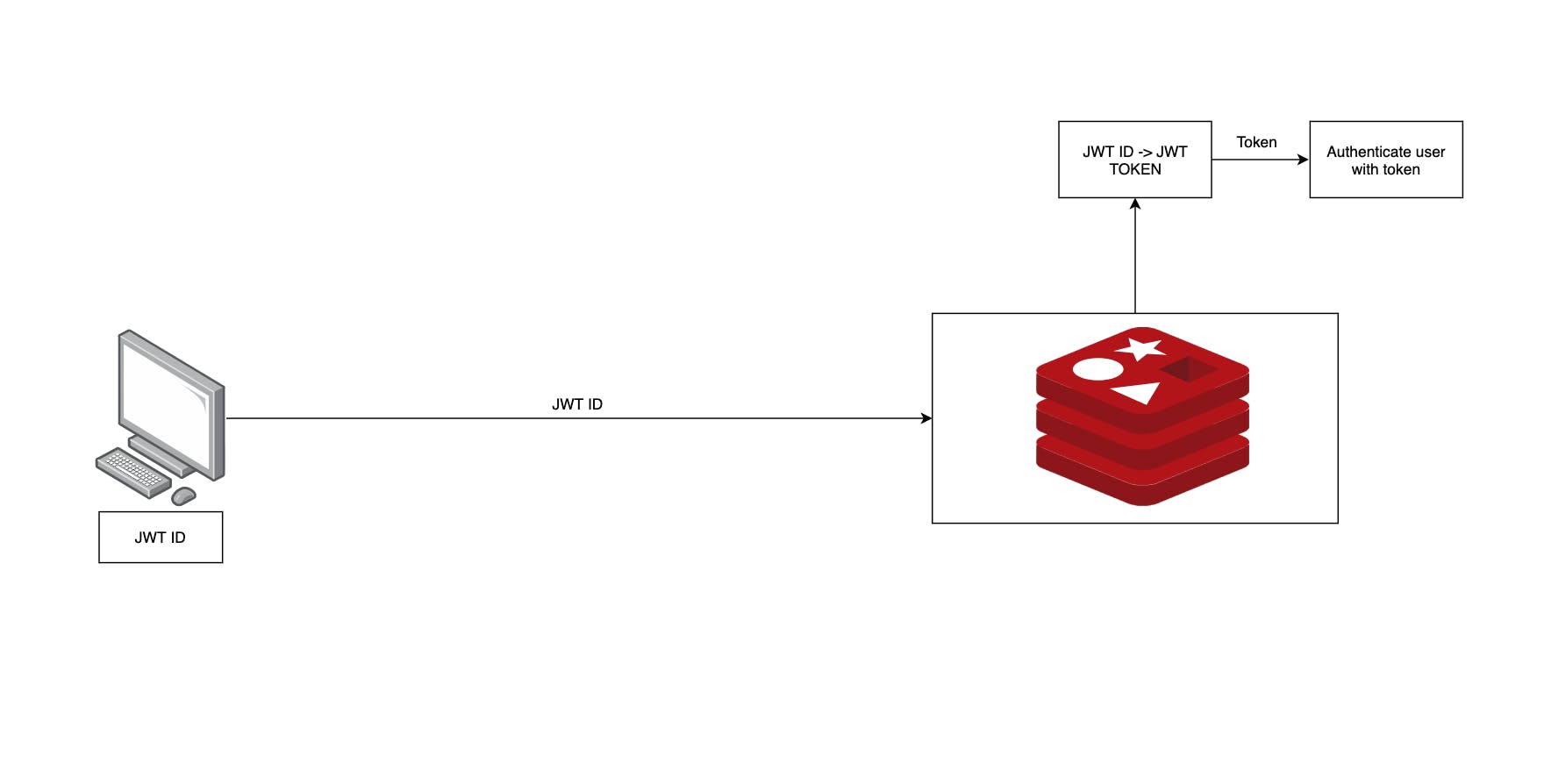
Initializing Redis variables
- We need to initialize redis variable say "counter" to 0 before starting.
- We'll be using this counter value to map tokens.
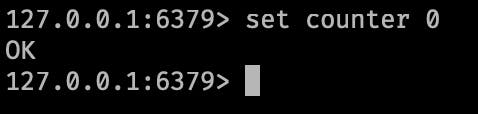
Creating a token
We can create a token using "jsonwebtoken" package in Nodejs, but before that, we need a user. To keep things simple, we can create a fakeUser object.
const fakeUser = {
name: "John",
email: "john@mail.com",
password: "pass1234"
};
- We need to increment the counter, so that we don't have any collisions.
- After incrementing, we can create a token using jwt.sign(...).
- Now, we can set the key as the counter and the value as the token.
client.get("counter", (err, data) => {
client.set("counter", parseInt(data) + 1);
jwt.sign(fakeUser, "secret", { expiresIn: "1d" }, (err, token) => {
client.set(parseInt(data) + 1, token);
res.cookie("jwt-id", parseInt(data) + 1);
return res.send("logged in");
});
});
We do parseInt(data) as Redis stores variables in the form of strings. We need an integer to increment which is why we need to parse it into an integer.
If this piece of code executes successfully, the output looks like this in redis-cli.
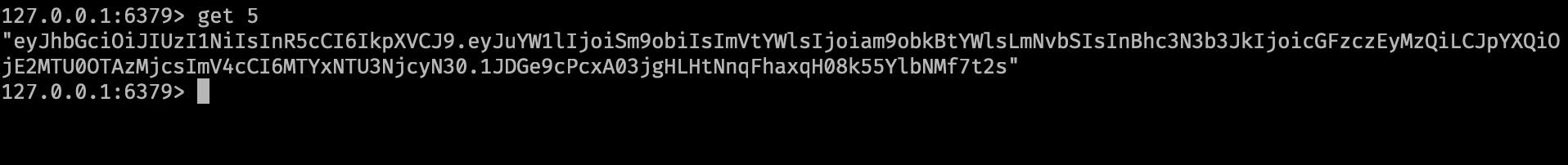
Verifying token and parsing token payload.
What is left is that we need to verify if this works. That'll be a POST request which means that the browser will send us the counter (id in this case).
- We need to get the token stored in the counter coming from the browser.
- Verify the token is valid using jwt.verify(...)
- The payload will be returning as a callback!
const { id } = req.body;
client.get(id, (err, data) => {
jwt.verify(data, "secret", async (err, payload) => {
console.log(payload);
});
});
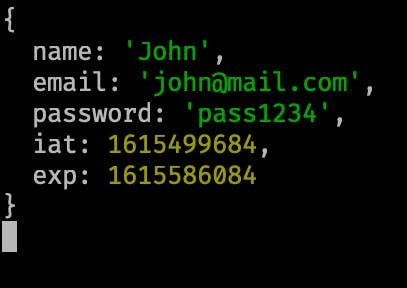
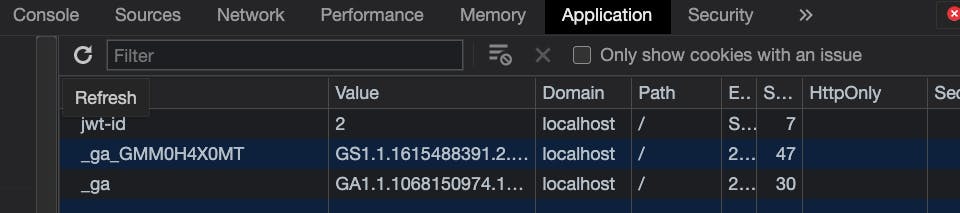
And, you can verify the jwt-id cookie in the browser itself.
Thanks for reading.
